Understanding the composition and characteristics of soil is crucial for a wide range of industries, from agriculture to construction and environmental science. Recent innovations in soil and core analysis have significantly improved our ability to assess soil properties quickly and accurately. This article delves into the advancements that are revolutionizing the field, offering insights into how these technologies can be applied effectively.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Importance of Soil Analysis
Soil analysis is fundamental in determining the suitability of a site for various uses, whether it’s for farming, building infrastructure, or assessing contamination levels. The data obtained from soil testing can influence crucial decisions about crop rotation in agriculture, foundation design in construction, and remediation strategies in environmental management.
Advancements in Auger Drilling
One of the significant advancements in the field of soil analysis is the use of auger drilling. This method involves the use of a rotating helical screw to bore into the earth and extract a sample. Auger drilling is particularly useful for soil sampling because it is less disruptive to the surrounding area compared to other drilling methods. It allows for quick and efficient soil core extraction, providing clear and uncontaminated samples from various depths.
Techniques in Soil Sampling
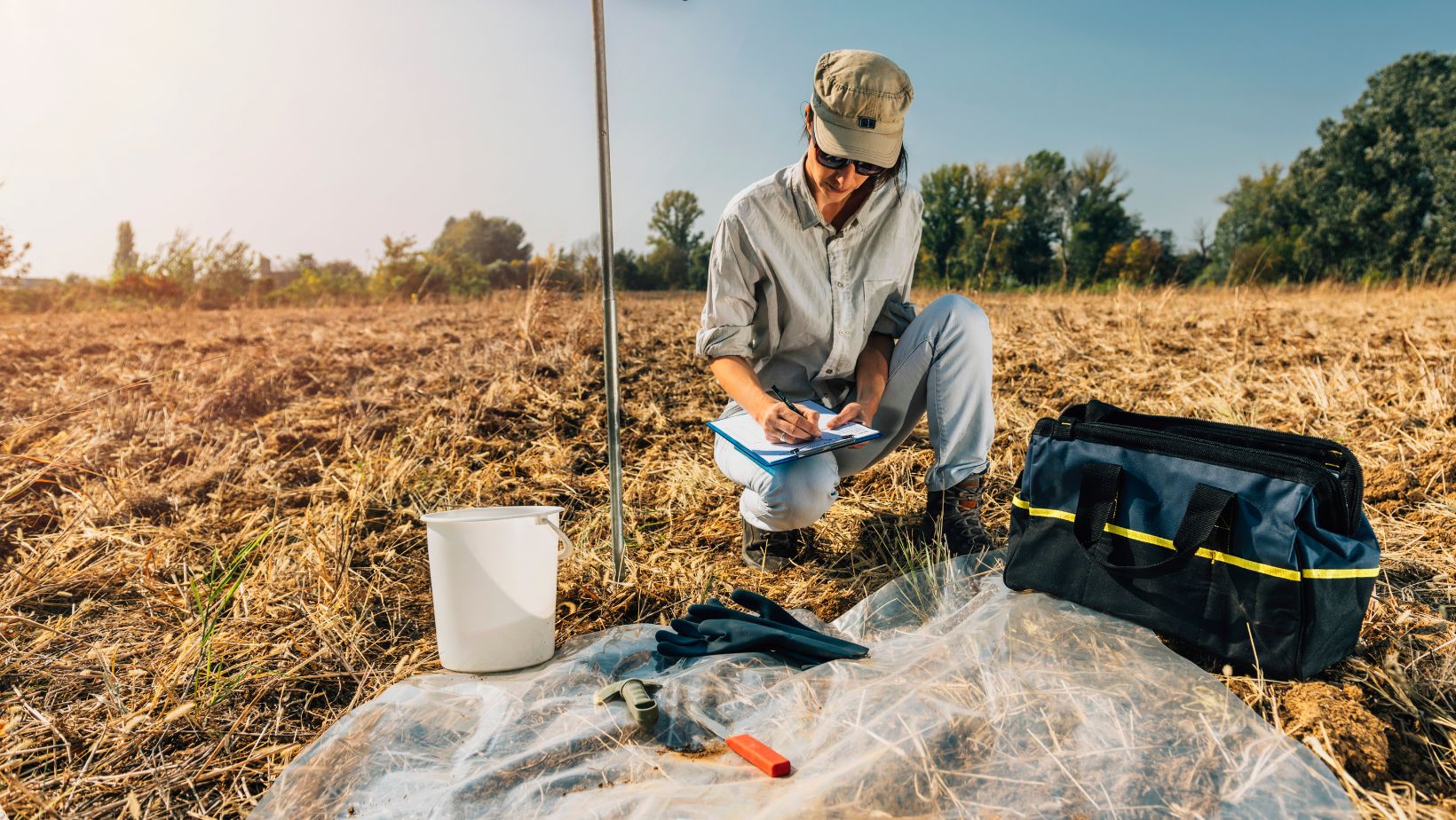
Accurate soil sampling is the first step in effective soil analysis. The method of sampling depends on the specific needs of the project and the characteristics of the soil.
Direct Push Technology
Direct push technology involves driving a hollow steel tube into the soil to collect samples. This method is fast and efficient, providing continuous soil cores with minimal disturbance. It’s particularly effective in softer soils where detailed stratigraphic profiling is required.
Soil Sampling Kits
For agricultural or garden testing, portable soil sampling kits are available. These kits often include tools for pH testing, moisture analysis, and nutrient profiling. They allow farmers and gardeners to perform immediate assessments on-site, aiding in quick decision-making for soil management.
Core Analysis Techniques
Once soil cores are extracted, detailed analysis can begin. This process involves several innovative techniques that can provide extensive data about the soil’s composition.
Spectroscopic Methods
Spectroscopy, particularly X-ray fluorescence (XRF), is used to determine the chemical composition of soil samples. This method can quickly analyze the mineralogy of the soil and detect trace elements, which is crucial for assessing soil health and pollution.
Laser Diffraction
Laser diffraction measures the size distribution of soil particles. This method is highly accurate and much faster than traditional sieving techniques.
Particle size analysis is vital for understanding soil texture, which affects water retention, nutrient availability, and aeration.
Thermal Analysis
Thermal analysis techniques, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), assess the thermal properties of soil. These methods can help determine organic matter content, mineral composition, and other thermal characteristics of the soil.
Applications of Soil Analysis
The data obtained from soil analysis has a wide range of applications across different fields. Here’s how different industries benefit from detailed soil and core analysis.
Agriculture
In agriculture, soil analysis is used to optimize crop yields by determining the nutrient needs of specific crops and tailoring fertilizer applications accordingly. It can also help in managing soil pH and salinity levels, which are crucial for crop health.
Construction and Engineering
In construction, soil analysis helps engineers design foundations appropriate to the soil conditions. It can prevent costly problems such as differential settling and ensure the longevity and safety of structures.
Environmental Science
In environmental science, soil analysis is critical for assessing contamination and determining the appropriate remediation techniques. It can help track pollution sources and assess the impact of industrial activities on soil health.
Future Trends in Soil Analysis
The future of soil and core analysis looks to even more automation and precision. Here are some emerging trends:
Drones and Remote Sensing
Drones equipped with sensors are increasingly being used for remote soil analysis. They can cover large areas quickly, providing valuable data on soil moisture, texture, and health without the need for extensive physical sampling.
Artificial Intelligence
AI and machine learning are beginning to play a role in interpreting soil data.
These technologies can predict soil behavior under various conditions and suggest optimal agricultural practices or construction approaches.
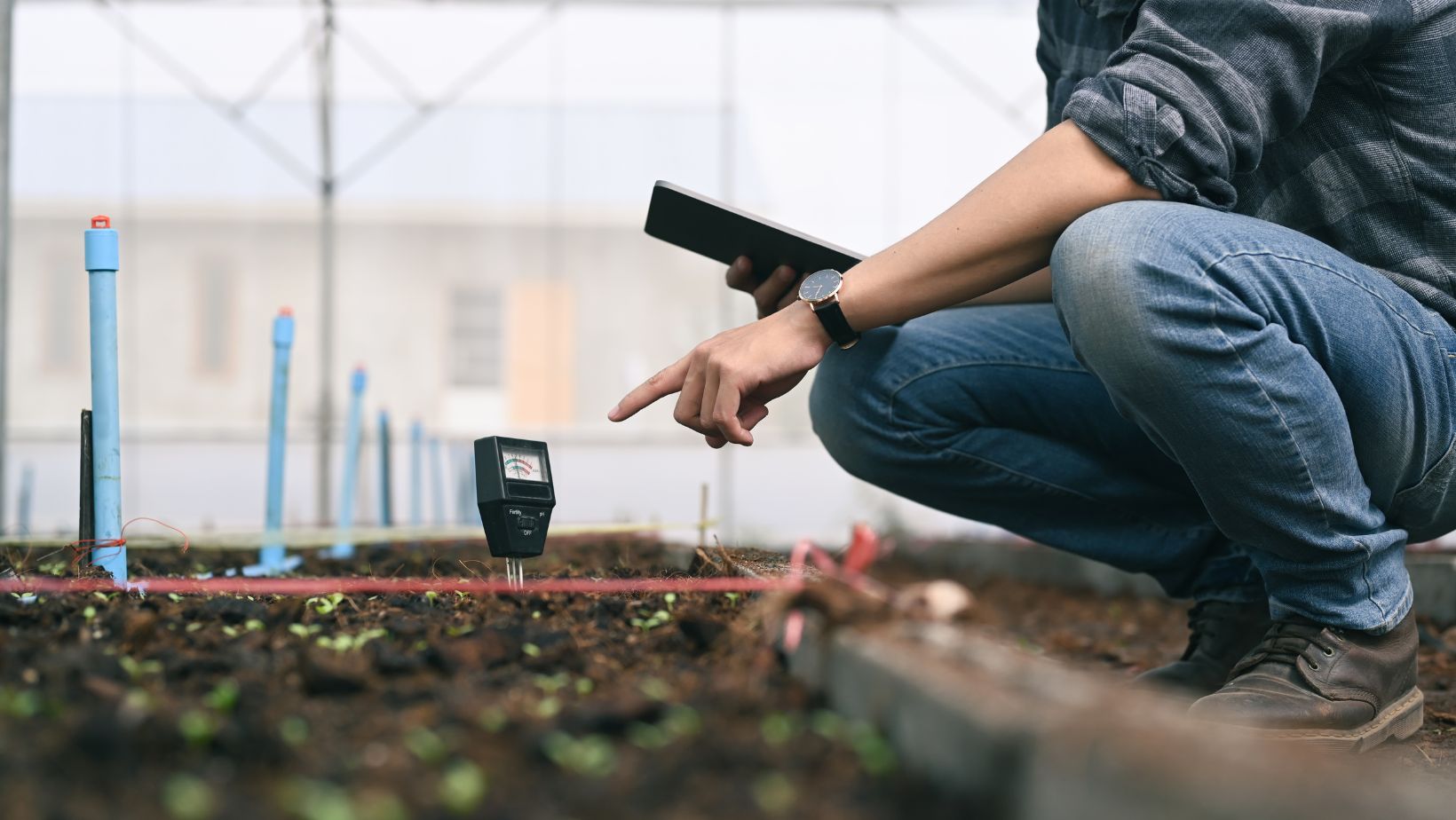
Portable Analyzers
The development of portable, high-precision soil analyzers will allow for real-time soil testing on a larger scale. This could revolutionize the way farmers, scientists, and engineers access and use soil data.
A Grounded Approach to Soil Analysis
As we continue to develop and refine the tools and techniques for soil and core analysis, our ability to understand and utilize the earth beneath our feet grows. Innovations like auger drilling, spectroscopic methods, and thermal analysis are not just enhancing our scientific capabilities—they are also providing practical solutions that impact agriculture, construction, and environmental management. By embracing these advancements, we can make more informed decisions that not only optimize our immediate objectives but also safeguard our environment for future generations.